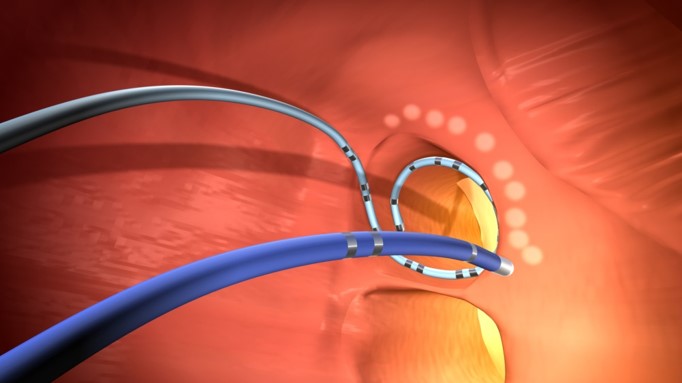
Catheter ablation is a procedure that can correct heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias). Catheter ablation works by a limited and controlled heating (or in some instances freezing) of the heart tissue that triggers or sustains an abnormal heart rhythm.
In some cases, cardiac ablation prevents abnormal electrical signals from entering your heart and, thus, stops the arrhythmia. Catheter ablation usually uses long, flexible tubes (catheters) inserted through a vein or artery in your groin and threaded to your heart to deliver energy in the form of heat or extreme cold to modify the tissues in your heart that cause an arrhythmia.
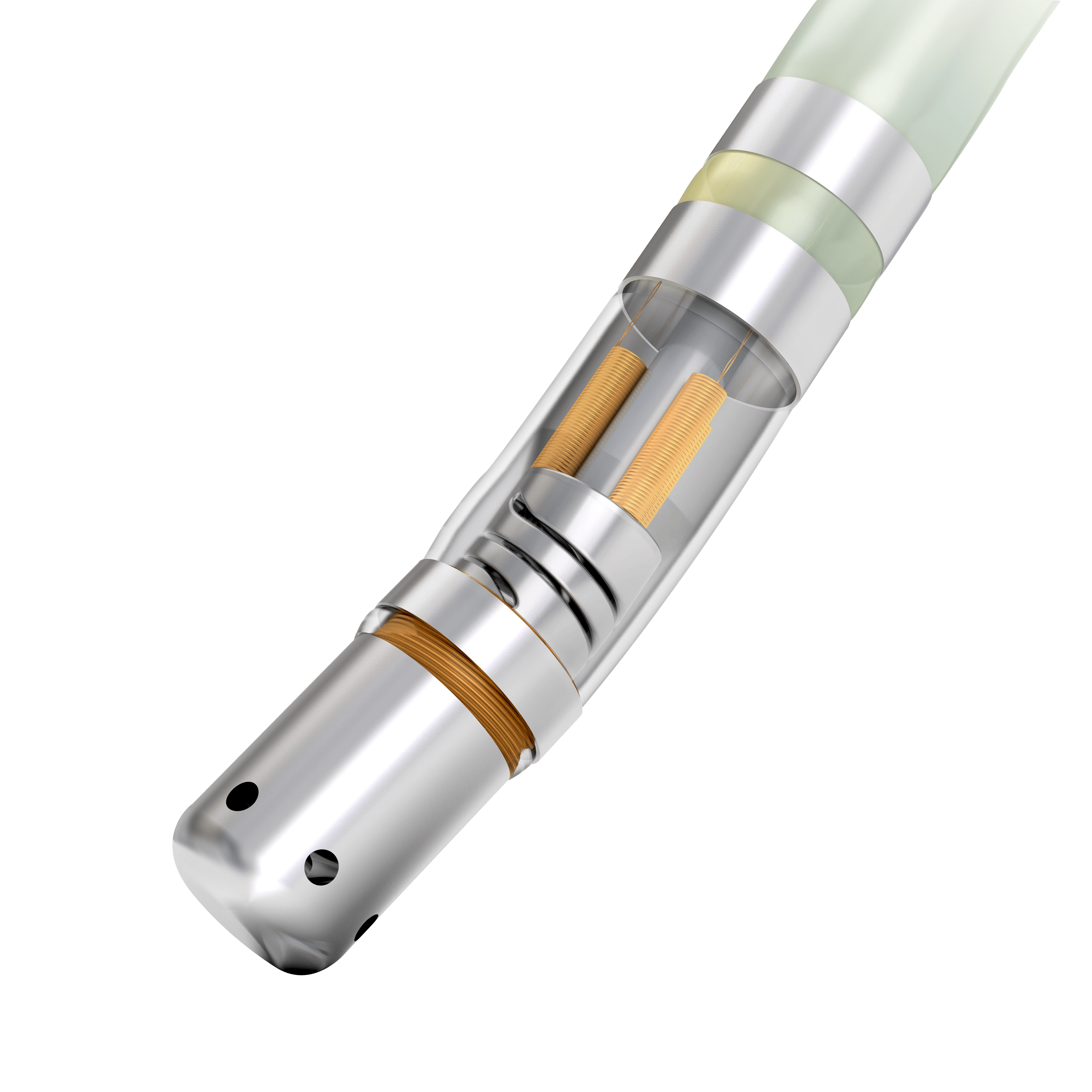

SmartTouch Catheter
Catheter ablation is sometimes done through open-heart surgery, but it’s often done using catheters, making the procedure less invasive and shortening recovery time. The catheters are often inserted through a site in the groin (upper thigh) or neck, and guided through the vein until they reach the heart. Small electrodes on the tip of the catheters stimulate and record the heart’s activity. This test, called an electrophysiology study (EPS), allows the doctor to pinpoint the exact location of the short circuit (mapping). Once the location is confirmed, the short circuit is either destroyed (to reopen the electrical pathway) or blocked (to prevent it from sending faulty signals to the rest of the heart). This is done by sending energy through the catheters to destroy a small amount of tissue at the site.
The energy may be either hot (radio-frequency or RF ablation), which cauterizes the tissue, or extremely cold, which freezes it (Cryo-ablation). Ablation is used to treat many types of arrhythmias. It is often successful in eliminating the need for long-term drug therapy. Ablation may be an option in many of the following cases: If your arrhythmia cannot be controlled with lifestyle changes or medication. If you cannot tolerate or do not want to take medication to treat your arrhythmia. If you have a supraventricular tachycardia(SVT), a rapid heartbeat that begins in the upper chambers of the heart. If you have ventricular tachycardia (VT), a rapid heartbeat that begins in the lower chambers of the heart. For VT, ablation is sometimes used in combination with an ICD.